Cervical osteochondrosis is the progressive dystrophic and deigenerative lesion of the intervertebral discs in the area of 1-7 vertebrae belonging to the cervical region.
As a result of cervical osteochondrosis, deformation, exhaustion, and then damage to the vertebral bodies occurs. This disrupts normal blood supply and nervous conductivity in the neck and in those areas that are innervated by the roots of the nerves of the cervical nerves.
Cervical osteochondrosis can be either isolated or combined with osteochondrosis of other departments - lumbar and sacral.
Reasons
The causes of dystrophic and degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs have not yet been sufficiently studied. The assumption that osteochondrosis is a senile phenomenon of confirmation. It is found even in children and adolescents.
A number of factors predisposing to the development of osteochondrosis are distinguished. These include:
- Sedomer and sedentary lifestyle,
- Sitting types of work with a static load on the neck,
- overweight, insufficient physical development,
- dysplastic processes of connective tissue,
- violation of blood circulation in the neck,
- neck injuries,
- Scoliosis, posture defects, uncomfortable pillows and mattresses,
- Hereditary predisposition, metabolic defects.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The cervical spine, due to the features of the skeleton, straightforwardness, as well as due to the large size of the head, is especially vulnerable to the development of osteochondrosis-the vertebrae in it are the smallest in comparison with other parts of the spine, and the muscle frame is not very pronounced.
The most characteristic symptom that patients complain about - pain in the cervical region. Depending on the damage zone, the pain may be localized
- in the collar and shoulder;
- throughout the cervical spine;
- On the front surface of the chest.
Pain for cervical osteochondrosis is due to the features of the cervical region.
The first signs of cervical osteochondrosis are insignificant and slightly specific:
- The pain in the neck in the evening,
- feeling of heaviness in the head, headaches in the occipital zone,
- a feeling of numbness or tingling in the shoulders and hands,
- Cryst in the neck when turning the head, clicking the vertebrae.
Leading symptoms:
Vegetative-Dystonic
- Quite severe pain in the neck and, especially, in the area just below the back of the head;
- pain occurs after a long stay in one position (for example, after sleep);
- The neck muscles are constantly tense;
- There are difficulties with abandonment of the hand to the side;
- On the affected side, the fingers are constrained in movements.
Since the vertebral arteries are compressed, neurological manifestations are observed: headache, nausea, fainting.
Spinal symptom
Pain is localized behind the sternum on the left.
This type of pain should be distinguished from pain as in angina pectoris (with angina pectoris, nitroglycerin is relieved, with osteochondrosis - no).
With a gradual violation of the structure of the intervertebral discs, their compression (compression) occurs and infringement of the roots of the nerves occurs, as well as narrowing or infringement of arteries and veins, which take place in the area of the vertebral bodies.
This leads to the formation of special syndromes - radicular and ischemic.
- The defeat of the roots of the first cervical vertebra (C1): violations affect the back of the head, reducing the skin sensitivity;
- lesion C2 gives pain in the crown of the crown and back of the head;
- The lesion of C3 gives pain in the neck from the side of infringement, a decrease in sensitivity in the tongue and sub -language muscles, in some cases with speech impairment and loss of control over the language;
- The defeat of C4 and C5 gives pain in the shoulder and clavicle, a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the head and neck, hiccups, respiratory disorders and pain in the heart;
- The defeat C6 is most often, giving pain from neck to shoulder blade, forearm, up to thumbs, the skin sensitivity can suffer:
- The defeat C7 gives similar symptoms with pain in the neck, back of the shoulder, up to the rear of the hand, violation of the strength of the hands and a decrease in reflexes.
Blood circulation disorders due to the compression of the vessels in the area of the cervical vertebrae give headaches up to migraine, severe dizziness, visual impairment and ears in the ears, flickering flies in front of the eyes, disorders of autonomic functions.

There may be manifestations of cardiac syndrome with compressive heart pain, lack of air and heartbeat, rhythm disorders.
Complications
Serious complications of cervical osteochondrosis are
- protrusion of intervertebral discs with the formation of a hernia (protrusion);
- rupture of the intervertebral disk with infringement of nerves and blood vessels, the compression of the spinal cord is possible, which can lead to death;
- There can also be radiculopathies (lesions of roots), the formation of osteophytes (spikes on the vertebrae) with a manifestation of paresis and paralysis.
Diagnostics
In the presence of the above complaints, an appeal to the orthopedic physician or neurologist is necessary.
First of all, the doctor will evaluate mobility and soreness in the neck, sensitivity and other functions. Then, radiography of the cervical spine in several projections will be required, if necessary, computed tomography or magnetic resonance scanning with suspicion of hernia.
In case of circulatory disorders, rheoencephalography and examination of the fundus will be needed.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Today, there are both traditional and non -traditional methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine.
Conservative methods are mainly used:
- Symptomatic therapy with analgesics to relieve pain syndrome
- Reception of anti-inflammatory drugs of Non-steraidal series-to relieve inflammation and edema of tissues
- To eliminate muscle cramps, antispasmodics and drugs to improve blood circulation are used.

In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, substances are used that restore the structure of intervertebral discs - Chondroproprotectors.
The course of vitamin therapy of group B is shown, the external products for therapy are applicable - gels and ointments, creams with anti -inflammatory and analgesic components. Shows stimulants of the regeneration of intervertebral discs.
Surpassed and general massage, acupuncture, physioception, physiotherapy and gymnastics and gymnastics helps in the treatment of osteochondrosis. The method of osteopathy has proven itself well - a mild effect on the "clamped" zones of muscles and vertebrae.
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, the wearing of a special collar (Shantsa collar) is recommended.
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis with hernias that violate sensitivity and blood circulation can be treated promptly.
The duration of treatment depends on the neglect of the condition, since osteochondrosis is a progressive chronic disease. Treatment can be long, and preventive courses are performed for life.
Proper nutrition will help to relieve the condition for osteochondrosis.
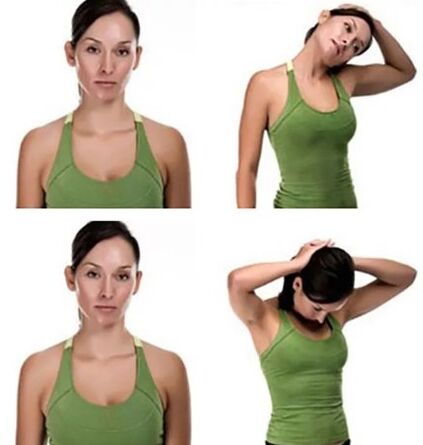
Exercises for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Self-ejecting: in a position with a straight back, it is necessary to lower the shoulders as low as possible, while the neck must be pulled up. It is necessary to make at least 10 approaches at least 3 times a day.
- Self -massage: Grace up the neck with a towel, taking it by the ends and pull it for them alternately, spreading the muscles of the neck. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the towel does not slide along the neck.
- Gymnastics for the cervical region for osteochondrosis: small bending of the neck, as well as turns and tilting of the head, are shown. At a time, 5-7 inclinations are made in each direction. This exercise is most useful to perform after self -massage of the cervical spine.
Prevention
The basis of the health of the cervical spine is a strong and healthy back, physical activity, a comfortable bed with anatomical pillows and mattress, proper posture and proper nutrition.
It is worth avoiding neck injuries and weight lifting. It is necessary to combine prolonged sitting with periods of rest and warm -up.